Introduction
Ring Main Units (RMUs) play a critical role in medium-voltage power distribution networks by ensuring reliable switching, protection, and continuity of supply. Most modern RMUs use SF₆ (Sulfur Hexafluoride) gas as an insulating and arc-quenching medium due to its excellent dielectric properties and operational reliability.
Proper SF₆ gas filling and pressure commissioning is essential for the safe operation, performance stability, and long service life of an RMU. Any deviation from the manufacturer’s specified gas pressure may compromise insulation strength and overall system safety.
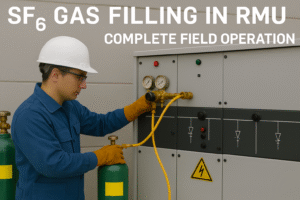
This article explains the complete field operation of SF₆ gas filling in an RMU, following standard industry practices and the professional execution methodology adopted by FK Engineering during site commissioning works.
Project Scope and Objective
The scope of SF₆ gas filling work typically includes:
- Filling the RMU gas compartment with SF₆ gas up to the manufacturer-recommended rated pressure
- Ensuring the gas system is airtight and free from leaks
- Verifying gas density and pressure indicators
- Preparing the RMU for final commissioning and energization
This activity is normally performed after mechanical installation and before electrical commissioning of the RMU.
Safety Precautions Before Gas Filling
Handling SF₆ gas requires strict adherence to safety and environmental guidelines. Prior to starting the operation, the following precautions must be ensured:
- The work area should be well ventilated
- Only trained and authorized personnel should handle SF₆ gas
- Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) such as safety gloves, goggles, and masks must be used
- Open flames and heat sources must be strictly avoided near the gas filling area
- Moisture and air ingress into the gas compartment must be prevented
Following these precautions minimizes health risks and ensures safe field operations.
Tools and Equipment Required
For a smooth and controlled gas filling process, the following equipment is required on site:
- SF₆ gas cylinder with pressure regulator
- Gas filling hose with compatible adapters
- Calibrated pressure gauge or gas density monitor
- Leak detection spray or electronic gas detector
- Torque wrench for valve tightening
- Gas recovery or evacuation arrangement (if applicable)
All tools must be inspected before use to ensure accuracy and safety.
Step-by-Step SF₆ Gas Filling Procedure
Step 1: Pre-Filling Inspection
Before connecting the gas cylinder:
- Confirm that RMU installation is mechanically complete
- Ensure all panels, interlocks, and earthing mechanisms are properly secured
- Check the gas pressure indicator to confirm low or zero pressure
- Verify that the gas filling valve is clean and undamaged
This inspection ensures readiness for safe gas filling.
Step 2: Hose Purging
To avoid air contamination:
- Connect the gas hose to the SF₆ cylinder
- Slightly open the regulator to allow a small quantity of gas to flow through the hose
- Purge out all trapped air before connecting the hose to the RMU gas valve
This step is critical to maintain gas purity inside the RMU.
Step 3: SF₆ Gas Filling Operation
- Connect the purged gas hose securely to the RMU filling valve
- Slowly open the gas cylinder regulator
- Monitor the RMU pressure gauge continuously during filling
- Fill gas gradually until the rated pressure specified by the manufacturer is achieved
- Close the gas cylinder valve once the required pressure is reached
Gas filling must be done slowly to avoid pressure overshoot and temperature-related errors.
Step 4: Post-Filling Inspection
After completion of gas filling:
- Disconnect the filling hose carefully
- Tighten the filling valve cap using the recommended torque
- Check the pressure or density indicator to confirm it is within the normal operating (green) zone
- Perform leak detection around valves and gas joints
Any pressure drop or leakage must be rectified before proceeding further.
Operational Checks and Commissioning Readiness
Once SF₆ gas filling is completed, the RMU is prepared for commissioning checks, including:
- Mechanical operation of load break switches and earthing switches
- Verification of interlocking mechanisms
- Inspection of protection devices and fuses
- Confirmation of gas pressure stability over time
These checks ensure the RMU is safe for energization and long-term operation.
Environmental Considerations
SF₆ gas is a potent greenhouse gas, and its release into the atmosphere must be avoided. Best practices include:
- Preventing gas leakage during filling and disconnection
- Using recovery systems where applicable
- Ensuring proper storage and handling of SF₆ cylinders
Responsible gas handling supports environmental protection and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
SF₆ gas filling in an RMU is a precision-based and safety-critical field operation. When executed systematically — including pre-inspection, controlled filling, leak testing, and final verification — it ensures:
- Reliable insulation performance
- Safe medium-voltage switching
- Extended service life of the RMU
Professional execution of SF₆ gas filling, as practiced by FK Engineering, guarantees compliance with industry standards and dependable operation of power distribution systems.
tags/keywords
#SF6GasFilling#RMUOperation#FieldOperation#GasHandling#ElectricalMaintenance#SwitchgearMaintenance
#SF6Handling