Introduction
KCIP (Korangi Creek Industrial Park) recently engaged FK Engineering for a comprehensive High Tension (HT) cable testing and fault rectification project. The HT cables supply critical loads in the industrial park, and any failure can cause costly downtime, safety risks, or disruption of operations. FK Engineering’s work ensured reliable power delivery, safety compliance, and long-term performance of the HT cable network at KCIP.
The project involved detecting problematic or deteriorated cable sections, performing diagnostic tests, repairing or replacing damaged segments, and verifying performance through rigorous re-testing.
Project Background
• Location: Korangi Creek Industrial Park (KCIP), Karachi
• Scope: Testing existing HT cable network + locating faults + rectification + final verification
• Cable Voltage Level: Typically, 11 kV / 33 kV HT cable (depending on KCIP specification)
• Duration: Scheduled outage / partial shutdown period, planned over 1-2 days to minimize impact
KCIP supplies multiple industrial units and infrastructure within its area. The HT cables run underground or through ducts, exposed to environmental stresses, mechanical stress, moisture, and sometimes suboptimal installation conditions. Faults in cables result in voltage drop, overheating, or breaks in supply.
Preparation & Planning
- Pre-Inspection & Cable Route Survey
FK Engineering mapped out all HT cable routes in KCIP, reviewed existing drawings, checked past maintenance records, identified suspect sections (due to age, visible damage, or repeated faults). - Safety & Work Permits
Safety first: isolation of the cable sections, lockout/tagout (LOTO), ensuring no live circuits in tested portion, using required Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), and securing work site. - Tools, Test Equipment & Spares Prepared
Included: Insulation resistance testers (Megger), HiPot / DC voltage test kits, fault locators / TDR (Time Domain Reflectometer), joints & terminations kits, cable‐splice materials, protective accessories. - Shutdown Planning & Coordination
Coordinated with KCIP electrical department, tenant factories, and control room. Established exact time window for power cutoff, communication of outage notices, ensuring critical services are minimally affected.
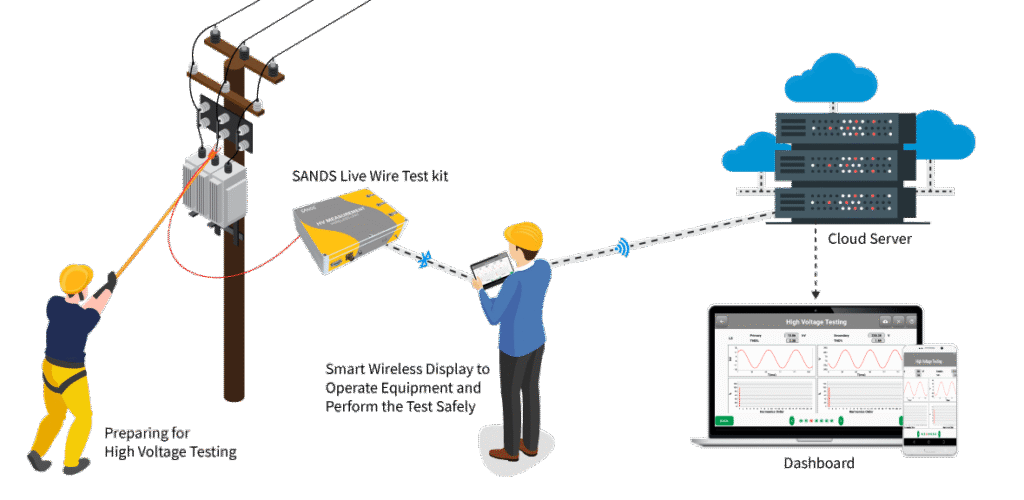
Technical Procedure / Testing & Rectification Steps
Below is a detailed summary of what FK Engineering did during the testing and fault rectification:
- Initial Insulation & Continuity Testing
• Perform Insulation Resistance (IR) test on each phase to earth, phase-to-phase, with appropriate megger voltage ( 5 kV for HT cables). This helps identify reduced insulation integrity. (Based on typical HT cable commissioning/test guides)
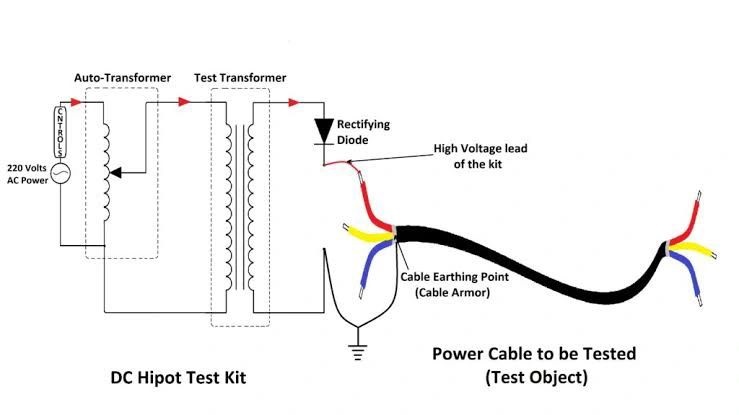
• Conduct continuity test to make sure conductors are intact. - High Potential (HiPot) / Dielectric Strength Test
• Apply a higher voltage than normal operating voltage (within safe standard limits) to test insulation under stress. Detects weak points, points of breakdown or leakages in insulation. (Referenced in test commissioning documents)
• Monitor leakage current during test. If leakage exceeds threshold, that segment is flagged for repair or replacement. - Fault Location / Pin-pointing
• Use Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) or other underground cable fault locators to precisely find where the fault or degradation is.
• For underground or ducted cables, moisture ingress, physical damage, or insulation breakdowns are common fault sources. - Inspection of Joints & Terminations
• After locating fault, open cable joints, inspect terminations, check connectors, insulation at joints, condition of cable sheath etc.
• Replace or refurbish joint kits to ensure proper sealing and electrical integrity. - Rectification / Repair
• Replace damaged cable segments if the length or damage is significant.
• For minor faults, apply splicing, re-insulation, or re-termination using industry standard kits.
• Ensure joints are properly sealed against moisture, mechanical protection is adequate. - Re-Testing / Verification
• Once repairs done, re-apply insulation resistance tests, HiPot test, continuity tests.
• Also perform load tests if feasible, to verify cable behaves under normal operational loads.
• Monitor cable during initial energization for thermal behavior, voltage drop, unusual heating.
Challenges & Solutions
Challenge Solution by FK Engineering
Locating underground fault accurately in long cable runs Use TDR / fault locators and route survey data; staging effort to isolate segments to test
Access to joints / terminations that are buried or embedded in difficult terrain Excavation, careful safety measures, use of weatherproof kits for joints
Moisture ingress / cable insulation degradation After repair, ensure proper sealing, use water-resistant insulation, applying protective sheath or coverings
Minimizing downtime / impact on KCIP tenants Precise scheduling, working during low load hours, prior notifications, optimizing team deployment
Outcomes & Benefits
After the project, KCIP observed:
• Reduced Fault Incidences: Previously recurring cable failures significantly decreased.
• Improved Electrical Safety: Insulation readings within safe limits; joints properly sealed; no abnormal leakage currents.
• Better Reliability & Uptime: More stable power supply to industrial units; fewer unplanned interruptions.
• Extended Cable Life: Early detection and repair prevented further deterioration which could have resulted in major cable replacements.
• Cost Savings: Avoided major replacement of long cable runs; reduced emergency repair costs; lowered maintenance overhead in medium term.
Best Practices & Guidelines
FK Engineering applied practices in line with international / industrial standards, such as:
• Conducting insulation resistance test, HiPot / Dielectric strength tests, as part of both preventative maintenance and after rectification.
• Use of fault locators (TDR) to accurately locate cable faults rather than guesswork or only visual inspection.
• Ensuring proper jointing and terminations using approved kits and correct installation methods.
• Maintaining documentation: test results before and after repairs, location of faults, type of repair, insulation values, etc.
• Safety first: isolation, PPE, proper permit & procedure for working with high voltage systems.
Recommendations for Future Work
• Establish a periodic maintenance schedule for HT cables: include insulation resistance, thermal imaging, and dielectric (HiPot) tests at regular intervals.
• Install monitoring systems: temperature sensing, moisture sensors, or smart sensors to detect early issues.
• Ensure cable ducts / trenches are maintained: drainage, protection from mechanical damages, avoiding exposure.
• Train onsite staff to recognize early warning signs (smell, heat, discoloration, partial discharge etc.).
Conclusion
The HT Cable Testing and Fault Rectification project at KCIP, Karachi, executed by FK Engineering, demonstrates how systematic testing, careful diagnostics, and precise repair work combine to improve electrical infrastructure reliability. For industrial zones like KCIP, where power reliability is critical, such maintenance ensures that operations continue without unwanted interruptions, safety is upheld, and costs are controlled over long term.
Tags / Keywords
#HTCableTesting #FaultRectification #KCIPKarachi #ElectricalMaintenance #CableDiagnostics #InsulationTesting #HiPotTest #TDRFaultLocation